Life Insurance
TAX-FREE RETIREMENT STRATEGY
… using Permanent Life Insurance.
What if you could:
Provide an income tax-free death benefit for the people who depend on you.¹
Defer taxes as your accumulated cash value grows, and
Potentially access that cash value using income tax-free policy loans and withdrawals, to use for retirement income or other needs.²
Strategies to Save for Retirement
Pre-Tax Strategy:
might include an Employer sponsored qualified plan, like a 401(k) plan. You don’t pay current taxes on contributions made to the plan and earnings grow tax-deferred. Later when you take retirement income the benefits are income taxable.
After-Tax Strategy:
when you set aside a portion of your after tax income into an account earmarked for retirement. Taxes are paid annually on any earnings. An example of this type of savings is a Certificate of Deposit.
Tax-Deferred Strategy:
when you set aside a portion of your after tax income for retirement, earnings on the account grow tax-deferred. When retirement income is taken, taxes are due on the tax-deferred gain. A Non-Deductible IRA or an annuity is an example of this type of savings.
Tax-FREE Strategy:
is similar to the Tax-Deferred Strategy: you set aside a portion of your after tax income, and earnings grow tax-deferred. Retirement income is received income tax-free. A Roth IRA³ is an example of this type of savings, while a second type of financial vehicle is permanent life insurance.
Tax-Free Strategies: a Closer Look at Permanent Life Insurance
Roth IRA: Permanent Life Insurance:
This is an excellent choice to begin with. For 2023, in order to contribute to a Roth IRA, your adjusted gross income must be less than $153,000 for single tax filers, and less than $228,000 for those married, and filing jointly. In 2023, contributions are limited to $6,500 per person, or $7,500 if you’re age 50 or older.
Permanent Life Insurance:
The primary purposes for purchasing permanent life insurance is for the death benefit protection that it provides. However, permanent life insurance offers the ability to build up tax-deferred cash value that can be accessed during your lifetime to generate a stream of retirement income – potentially income tax-free⁴.
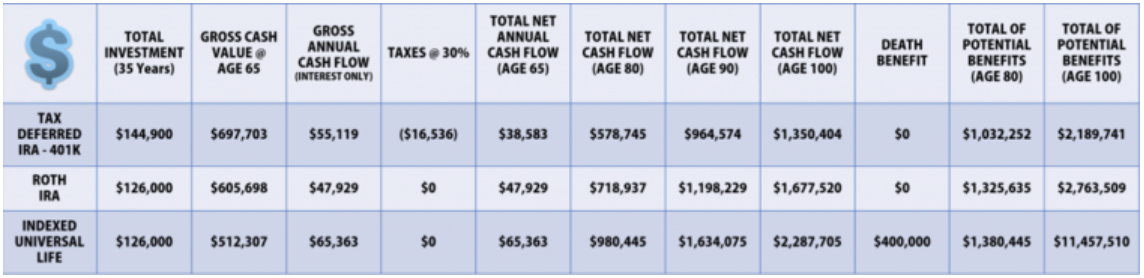
Real word example:
The below example shows $345 per month saved for 35 years…three ways – all at the same rate of 7.9%:
The pre-tax plans accumulate a higher balance at retirement, as you can see with the $697,703 gross value in the third column vs. $605,698 for Roth and $512,307 for IUL.
In the end, however, all that really matters is what you get to spend!
And assuming a combined tax rate of 30% the net after tax values in the fifth column show $38,585 for the pre-tax plans, $47,929 for the Roth and $55,363 for the IUL. Tax planning is critical and deferring the tax break until retirement looks to be the new default “best” way to structure a retirement plan.
Additional Benefits of Permanent Life Insurance
Self Completing:
In the event of a premature death, the income tax-free death benefit would help fund your spouses retirement goals.
Access to funds in the event of illness:
Accelerated Benefit Riders6 are available at no additional cost and may allow you to access all or a part of your death benefit to help pay for costs associated with a terminal, chronic or critical illness.
Protection in the event of disability:
For an additional fee, many policies offer an optional Waiver of Premium Rider that continues to pay your planned premiums if you became permanently disabled, keeping your policy on track with your original accumulation goals.
So which option is best for you?
For many people, a Roth IRA is a great tool. However, as mentioned earlier, there are some restrictions as to how much you can contribute and how much income you are allowed to have in order to qualify for a Roth IRA. It may even be that a combination of the two works best for you.
If you meet the income eligibility requirements for a Roth IRA, but want to set aside more than the contribution limits allow and you have a need for protection, you may want to do both a Roth IRA and Permanent Insurance. Contribute the maximum you can under the Roth and then apply the excess amount to your life insurance coverage.
Sources
*Examples shown (other than CD): No bank guarantee; Not a deposit; Not FDIC/NCUA insured; May lose value; Not insured by any federal or state government agency.
1 Internal Revenue Code § 101(a)(1). There are some exceptions to this rule. Please consult a qualified tax professional for advice concerning your individual situation.
2 The use of cash value life insurance to provide a tax-free resource for retirement assumes that there is first a need for the death benefit
protection. Policy loans and withdrawals reduce the policy’s cash value and death benefit and may result in a taxable event. Withdrawals up to the basis paid into the contract and loans thereafter will not create an immediate taxable event, but substantial tax ramifications could result upon contract lapse or surrender. Surrender charges may reduce the policy’s cash value in early years.
3 To qualify for the federal tax-free and penalty-free withdrawal of earnings, a Roth IRA must be in place for at least five years, and the distribution must take place after age 59½ or due to death, disability, or a qualified special purpose distribution, which is a qualified first-time home purchase (up to a $10,000 lifetime maximum). Depending upon state law, Roth IRA distributions may be subject to state taxes.
4 Internal Revenue Code § 101(a)(1). There are some exceptions to this rule. Please consult a qualified tax professional for advice concerning your individual situation.
5 Policy loans and withdrawals will reduce the policy’s cash value and death benefit and may result in a taxable event. Surrender charges may reduce the policy’s cash value in the early years. Withdrawals up to the basis paid into the contract and loans thereafter will not create an immediate taxable event, but substantial tax ramifications could result upon contract lapse or surrender. Policy loans will be taxed as ordinary income if the policy is allowed to lapse. It is possible that coverage will expire when either no premiums are paid following the initial premium, or subsequent premiums are insufficient to continue coverage.
6 Payment of Accelerated Benefits will reduce the Cash Value and Death Benefit otherwise payable under the policy. Receipt of accelerated benefits may be a taxable event and may affect your eligibility for public assistance programs. Please consult your personal tax advisor to determine the tax status of any benefits paid under this rider and with social service agencies concerning how receipt of such a payment will affect you. There is generally no restriction placed on the use of the benefit received. Riders are supplemental benefits that can be added to a life insurance policy and are not suitable unless you also have a need for life insurance. Riders are optional, may require additional premium and may not be available in all states or on all products. This is not a solicitation of any specific insurance policy.
Let’s Discuss!
Complimentary Policy Review & Consultation
Arizona Insurance Exchange is an independent agency, which means we are not beholden to any of the national firms. This independence affords us the ability to obtain the best coverage or product for your specific needs.
Please reach out to us using the links below so that we may provide you with a no-cost, no-obligation review of your current portfolio. We look forward to assisting you with your insurance, annuity, and retirement needs.